

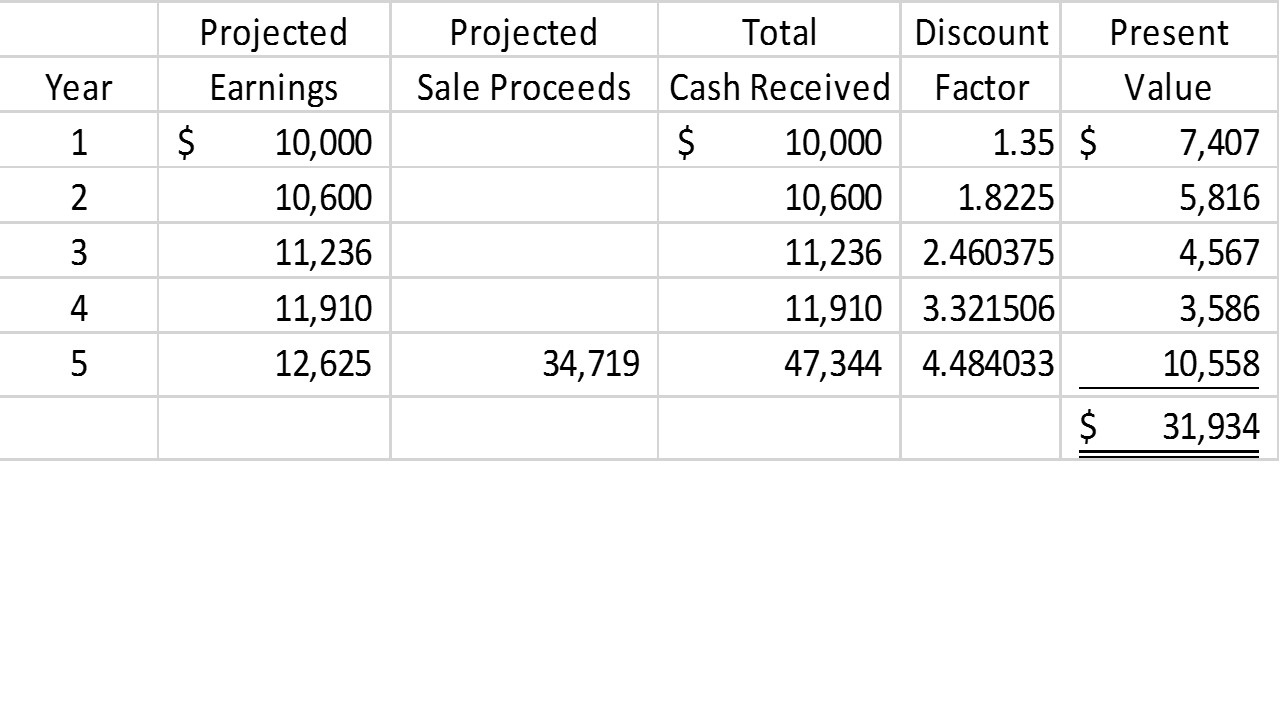
To conduct a DCF analysis, assumptions must be made about a variety of factors, including a company’s forecasted sales growth and profit margins (its cash flow) as well as the rate of interest on the initial investment in the business, the cost of capital and potential risks to the company’s underlying value (aka discounted rate). How do you conduct discounted cash flow analysis? It does this by adjusting for the time value of money-which assumes a dollar invested today is worth more than a dollar invested tomorrow because it’s generating interest over that period.

In other words: It looks to answer the question, “How much money will I get from this investment over a period of time and how does that compare to the amount I could make from other investments?”
Discounting cashflows present value free#
It establishes a rate of return or discount rate by looking at dividends, earnings, operating cash flow or free cash flow that is then used to establish the value of the business outside of other market considerations. What is discounted cash flow analysis?ĭiscounted cash flow analysis is an intrinsic valuation method used to estimate the value of an investment based on its forecasted cash flows. Here’s a quick overview of how discounted cash flow analysis works, and why it’s important to use in conjunction with public and private comps whenever assessing the value of a business. When used along with an intrinsic valuation method like discounted cash flow analysis-which looks at the value of an investment based on its projected future cash flows-these models can help investors, business owners and transaction advisors gauge a company’s current market value and then assess if that company is under- or overvalued. Previously, we looked at how private and public comps help analysts compare companies in a similar growth stage and industry to determine a company’s current market value. How do you know how much an investment is worth? Conducting a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis is the best way to arrive at an educated guess, whether you’re looking at the cost for a specific project, purchasing shares of a publicly traded company or investing in a private business.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
